United to form Auto Union AG
With the onset of the global economic crisis, the automotive market collapsed and many companies from the pioneering days of the motorcar disappeared. In 1932, at the initiative of Saxony’s state bank, the four manufacturers Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer joined forces to form Auto Union AG, in order to ensure their survival as a group. They succeeded in doing so by exploiting synergies in development and production and by cleverly carving up the market segments between the individual brands.
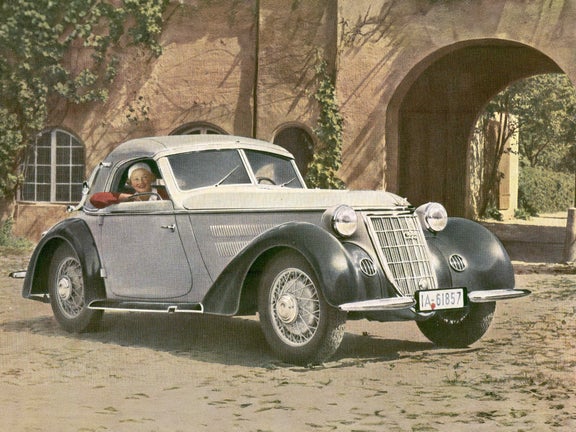
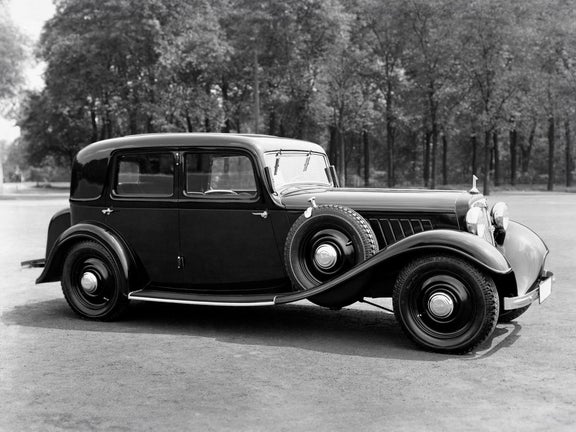
Audi Front UW (1933-1934)
More details
Audi Front UW:
- Engine: Petrol engine, 6 inline cylinders
- Displacement: 1,963 cm³
- Power output: 40 PS at 3,500 rpm
- Top speed: 100 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,500/1,650/1,575 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,300 kg
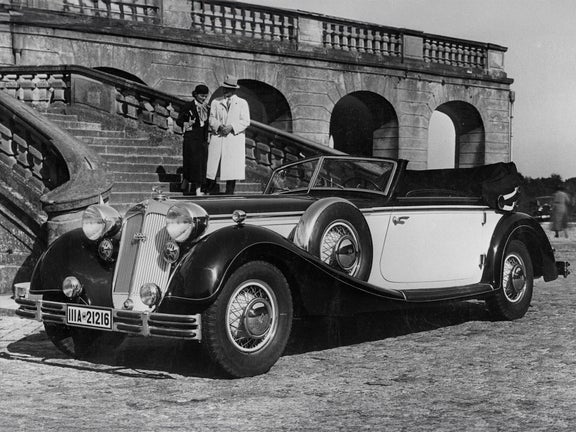
Horch 853 (1935-1937)
More details
Horch 853:
- Engine: Petrol engine, 8 inline cylinders
- Displacement: 4,944 cm³
- Power output: 100 PS at 3,400 rpm
- Top speed: 135 km/h
- Length/width/height: 5,350/1,830/1,550 mm
- Unladen weight: 2650 kg
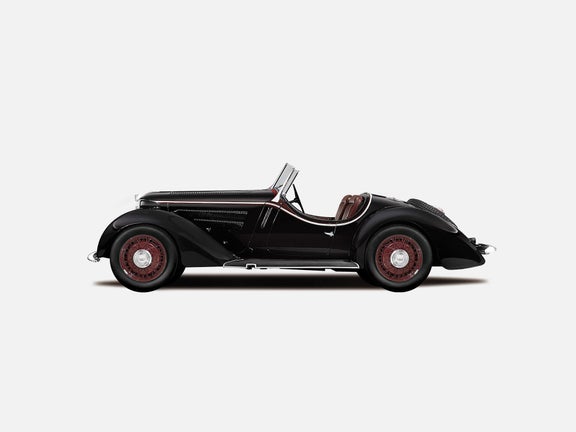
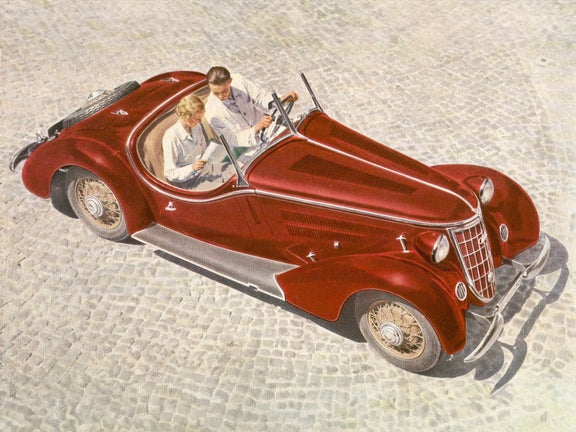
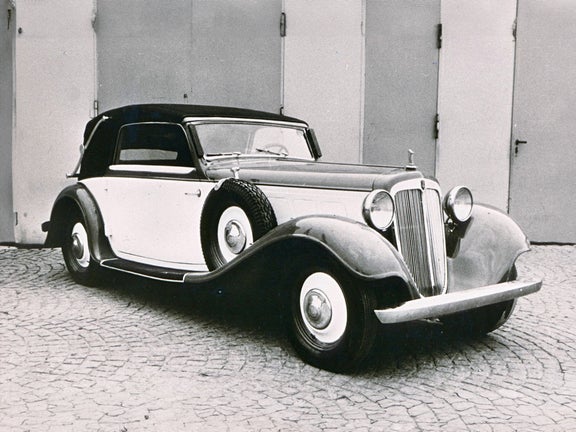
Wanderer W 25 K (1936-1938)
More details
Wanderer W 25 K:
- Engine: Petrol engine, 6 inline cylinders with compressor
- Displacement: 1,963 cm³
- Power output: 85 PS at 4,000 rpm
- Top speed: 145 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,360/1,670/1,390 mm (roadster)
- Unladen weight: 1,175 kg (roadster)
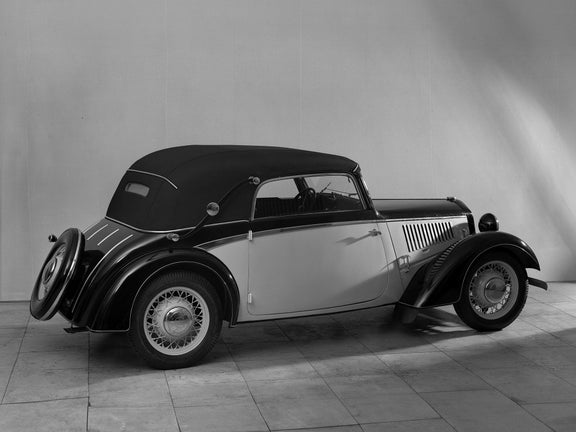
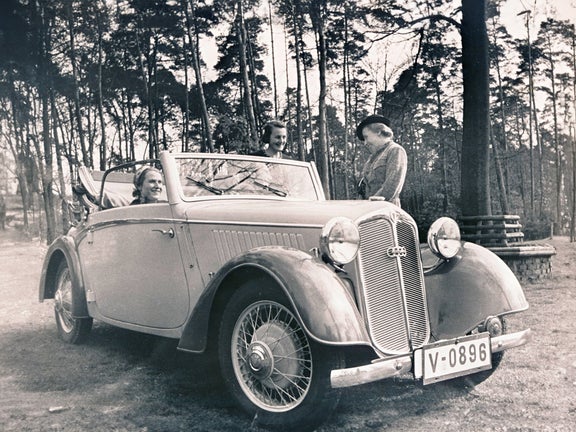
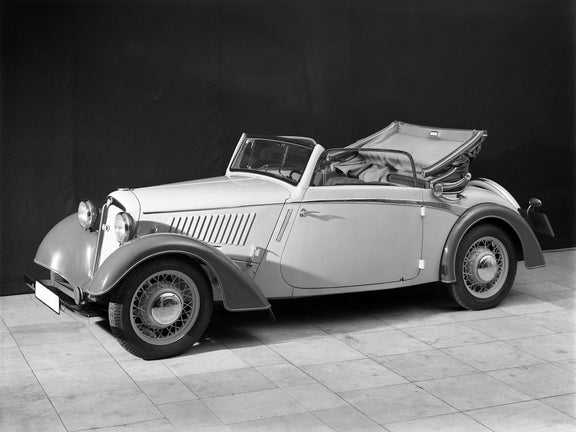
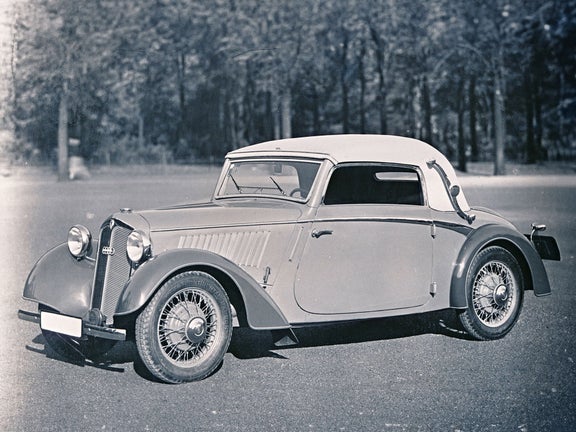
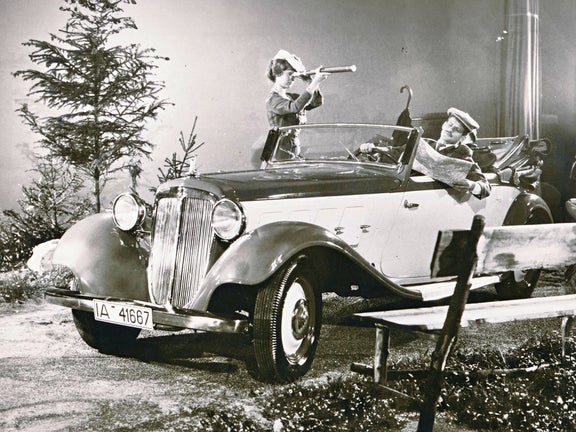
DKW F 5 (1935-1938)
More details
DKW F 5 Meisterklasse:
- Engine: Two-stroke petrol engine, 2 inline cylinders, transversely mounted
- Displacement: 690 cm³
- Power output: 20 PS at 3,500 rpm
- Top speed: 85 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,000/1,450/1,470 mm (limousine)
- Unladen weight: 800 kg (limousine)







.jpg?width=576)