Ascent to the premium segment
The 1980s and 1990s brought several technical innovations that allowed the brand with the four rings to position itself higher up in the market. Optimised aerodynamics, highly efficient engines, the modern ASF aluminium lightweight construction concept and, above all, the quattro permanent all-wheel drive system – which is still a hallmark of the brand today – set new standards. For the first time, Audi expanded its model range into the luxury and sports car segments. One of the Ingolstadt-based company’s new models in this area was the Audi TT, a timeless design icon.
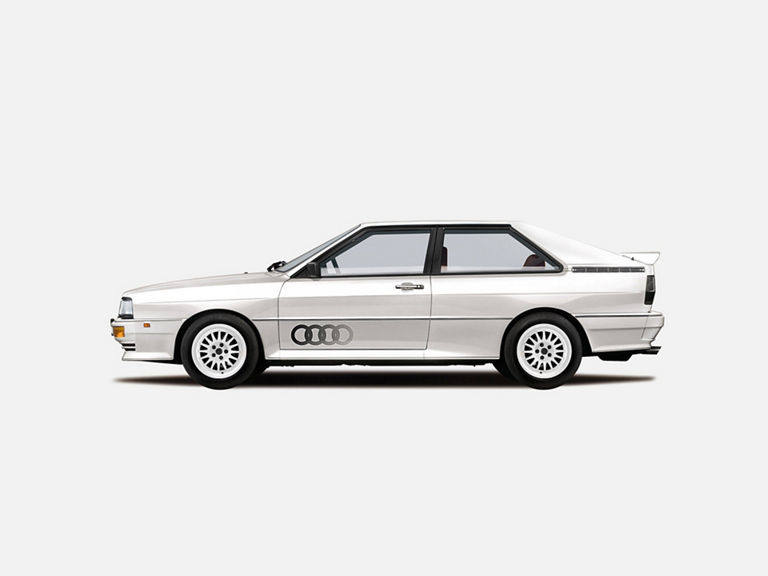
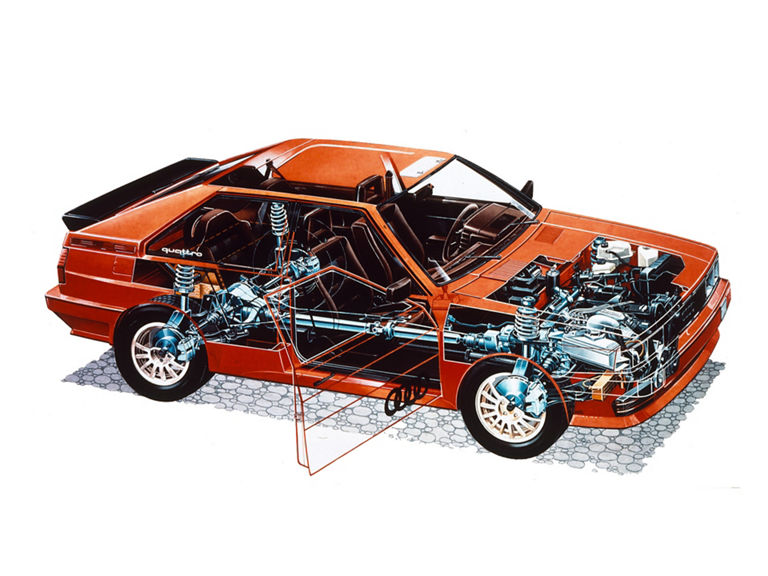
Audi quattro (1980-1991)
More details
Audi quattro:
- Engine: Petrol engine, 5 inline cylinders, turbocharging
- Displacement: 2,144 cm³
- Power output: 147 kW/200 PS at 5,500 rpm
- Top speed: 222 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,404/1,720/1,340 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,290 kg
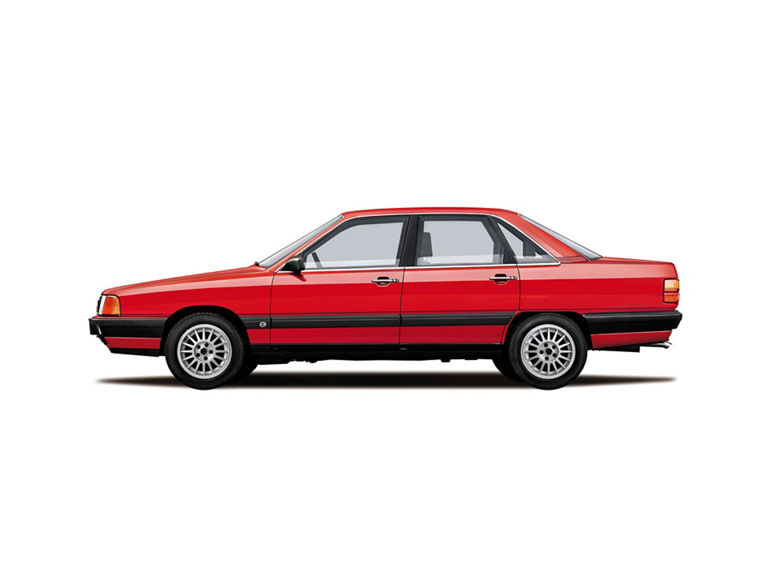
Audi 100 (1982-1991)
More details
Audi 100 TDI (C3):
- Engine: Diesel engine, 5 inline cylinders, direct injection, turbocharging
- Displacement: 2,460 cm³
- Power output: 88 kW/120 PS at 4,250 rpm
- Top speed: 200 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,793/1,814/1,421 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,320 kg
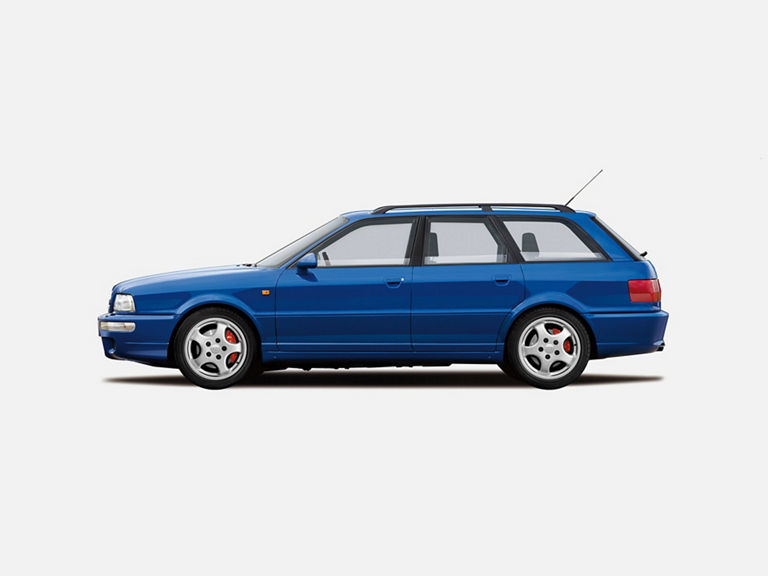
Avant RS 2 (1994-1995)
More details
Avant RS 2 (B4):
- Engine: Petrol engine, 5 inline cylinders, turbocharging
- Displacement: 2,226 cm³
- Power output: 232 kW/315 PS at 6,500 rpm
- Top speed: 262 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,509/1,695/1,386 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,595 kg
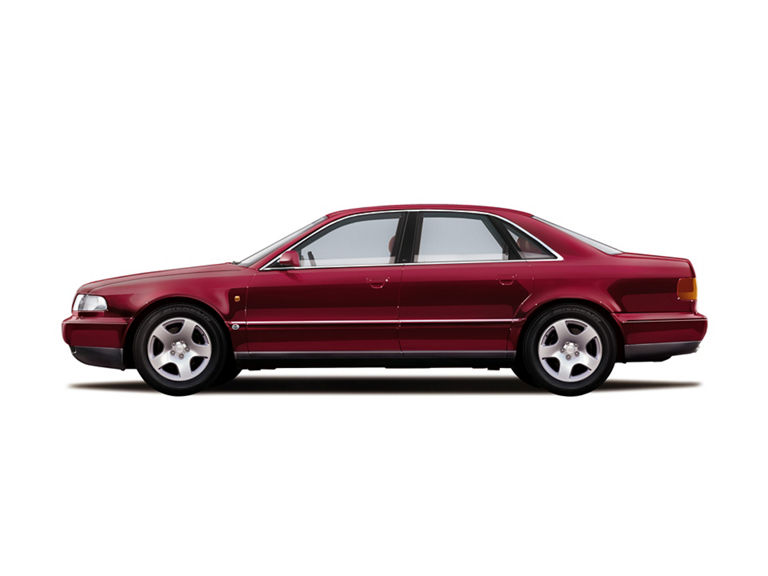
Audi A8 (1994-2002)
More details
Audi A8 4.2 quattro (D2):
- Engine: Petrol engine, 8 cylinders in a V configuration
- Displacement: 4,172 cm³
- Power output: 220 kW/300 PS at 6,000 rpm
- Top speed: 250 km/h
- Length/width/height: 5,034/1,880/1,440 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,750 kg
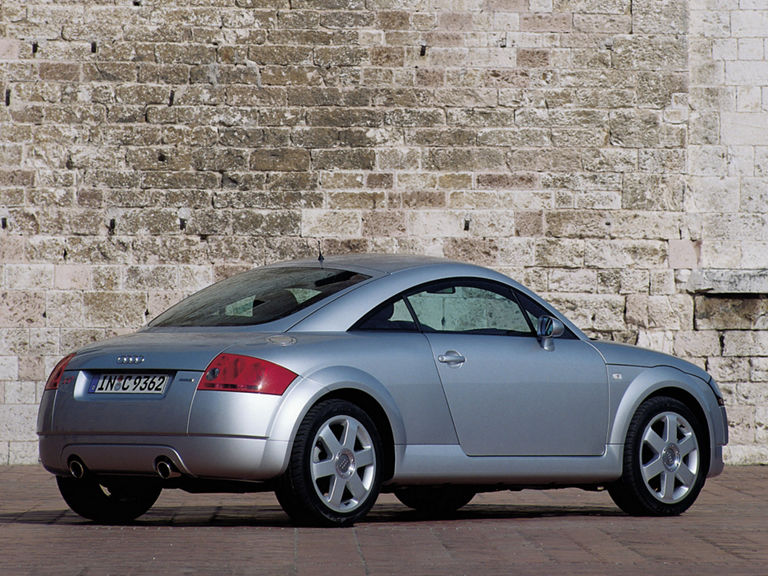
Audi TT (1998-2006)
More details
Audi TT 1.8 T (8N):
- Engine: Petrol engine, 4 inline cylinders, 20 valves, turbocharging
- Displacement: 1,781 cm3
- Power output: 132 kW/180 PS at 5,800 rpm
- Top speed: 228 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,041/1,764/1,346 mm
- Unladen weight: 1,280 kg
-Innenansicht-(Vordersitze)-1980.jpg?width=768)

-Fahraufnahme-1980.jpg?width=768)
-Ansicht-Motorraum-1980_3.jpg?width=768)
-Heckansicht_1.jpg?width=768)

-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)
-1988.jpg?width=768)
-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)
-Front-Seitenansicht-(rechts).jpg?width=768)

-Heckansicht.jpg?width=768)
.jpg?width=768)
-Frontansicht_2.jpg?width=768)
-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)

-Seitenansicht-(rechts)-1994.jpg?width=768)
-1994.jpg?width=768)
-Motorraum.jpg?width=768)
.jpg?width=768)

-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)
-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)




